Knee Replacement
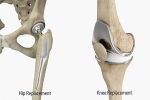
The knee is largest joint in the body and plays an important role in performing most daily activities. It is made up of three bones, the thighbone, shinbone and patella, which articulate with each other to form the knee joint. The smooth movement of this joint is facilitated by smooth articular cartilage that lines the bone ends. Damage to this cartilage can lead to knee arthritis. Total knee replacement is the surgical treatment for severe knee arthritis where the damaged knee is removed and replaced with an artificial knee implant. Partial knee replacement is a smaller operation which can sometimes be an option when the arthritis is limited to only one part of the knee. Modern surgery techniques now enable the implants to be inserted very accurately with excellent long term results. Improved methods of anaesthetic, pain relief, and rehabilitation also mean that that recovery can be achieved more quickly and with less pain than in the past. Dr Bauze performs partial and total knee replacement surgery at Sportsmed, Calvary North Adelaide and Calvary Wakefield Hospitals.
Blog: Less Pain and Faster Recovery after Knee Replacement Surgery
Over the last two years I have introduced an Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) pathway for knee replacement surgery at Sportsmed Hospital. This is a patient focused evidence-based team approach to knee replacement surgery that speeds up recovery and reduces pain and complications. Every aspect of patient care has been carefully evaluated and the patient is involved as an active participant in the process.
Blog: Independent audit shows low infection rate for joint replacements at Sportsmed
An independent audit by the Australian Orthopaedic Association National Joint Replacement Registry has confirmed that Sportsmed has an extremely low revision surgery rate for infection of joint replacements compared to the national average of all other hospitals. The audit covered 19223 joint replacement procedures performed at Sportsmed over 20 years from January 1999 to February 2019.
Blog: What's so good about Computer Navigated Knee Replacements?
Anyone who has been following my blog will know how much I like computer navigation for knee replacements. I frequently get asked why I am so passionate about it. There are lots of claims being made about new technologies available for knee replacements so making a decision about your knee can be very confusing. The bottom line is that computer navigation is the only technology that has been proven to improve the alignment, functional outcomes and long term results of knee replacements.
Blog: Hip and Knee Replacements – What Really Matters?
For most patients the key question when having a hip or knee replacement is "How long will it last?"
It is now easy for Australian surgeons to answer this question thanks to the long term data on revision rates recorded by the Australian Orthopaedic Association National Joint Replacement Registry (AOANJRR). A revision is when an operation is performed to change one or more joint replacement components due to complications or other issues with the joint. The latest report shows that the average revision rate of hip and knee replacements at 10 years is approximately 5-10%. There is however a lot of variation depending on the implant used and the surgeon.
Clinical Outcomes
Joint Replacement Revision Rates:
| Revision Rate | Dr Bauze | National Average |
| Total Knee Replacement at 8 years | 1.6% | 4.5% |
| Total Hip Replacement at 8 years | 4.1% | 4.4% |
How Much Does Knee Replacement Surgery Cost?
Out of pocket expenses for Knee Replacement Surgery vary by thousands of dollars depending on your choice of surgeon and where you have surgery. There is no evidence that higher costs result in better outcomes for patients. It pays to shop around. I have always made sure that the my fees are reasonable and transparent. As a result I frequently treat patients from South Australia as well as those travelling from interstate and overseas who have done their research on pricing and quality.
Total Knee Replacement (TKR)
Total knee replacement, also called total knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure in which the worn out or damaged surfaces of the knee joint are removed and replaced with artificial parts.
Partial Knee Replacement
Unicompartmental knee replacement is a minimally invasive surgery in which only the damaged compartment of the knee is replaced with an implant. It is also called a partial knee replacement.
Patellofemoral Knee Replacement
Patellofemoral knee replacement surgery may be recommended by your surgeon if you have osteoarthritis contained to the patellofemoral compartment and you have not obtained adequate relief with conservative treatment options.
Revision Knee Replacement
Revision knee replacement surgery involves replacing part or all of your previous knee prosthesis with a new prosthesis. Although total knee replacement surgery is successful, sometimes the procedure can fail due to various reasons and require a second revision surgery.
************************************************************************************
Blog: "Patient Specific" Knee Replacements – not so good after all?
There are several competing techniques available for knee replacement surgery. For the last eight years some Orthopaedic surgeons and implant companies have been heavily marketing so called ‘patient specific’ knee replacement surgery as providing improved accuracy and outcomes. I have been telling my patients that the evidence is simply not there to justify these claims whereas there is good evidence that computer navigation does reduce revision rates in knee replacements. The verdict is now in and the highly respected Australian Orthopaedic Association National Joint Replacement Registry (AOANJRR) has just reported that this ‘patient specific’ technique actually performs worse than other techniques.
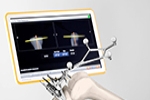
Blog: Is Robotic Joint Replacement Surgery Safe?
Robot technology in hip and knee replacement surgery has created a lot of interest in Adelaide this year. There are two types of systems available or in development - large robotic arms that position the cutting tool for the surgeon and smaller hand held instruments that the surgeon positions while the robot retracts the cutting tool if it is in the wrong place.
What's New in Knee Replacement?
For a patient considering knee replacement surgery, there are new developments under study which can help enhance their quality of life. These include:
- Use of Cementless parts that allow new bone to grow into a porous prosthesis and hold the parts in place, creating a biologic fixation
- Use of bioactive joint surfaces such as hydroxyapatite
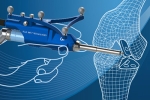
Computer Navigation for Total Knee Replacement
A total knee replacement surgery is the last resort to relieve pain and restore function in knee damaged by arthritis or an injury when non-surgical treatments do not relieve the condition.
Robotic Assisted Partial Knee Surgery
Robotic assisted partial knee surgery is an innovative alternative to the conventional surgical procedure in patients suffering from degenerative knee diseases such as osteoarthritis.
Minimally Invasive Total Knee Arthroplasty
Minimally invasive total knee arthroplasty is performed under sterile conditions in the operating room under spinal or general anesthesia. You will be lying on your back on the operating table with a tourniquet applied to your upper thigh to reduce blood loss.
Unicompartmental Knee Replacement
Unicompartmental knee replacement is a minimally invasive surgery in which only the damaged compartment of the knee is replaced with an implant. It is also called a partial knee replacement. The knee can be divided into three compartments: patellofemoral, the compartment in front of the knee between the knee cap and thigh bone, medial compartment, on the inside portion of the knee, and lateral compartment which is the area on the outside portion of the knee joint.